Obesity Complications, Body Mass Index (BMI), and Bariatric Surgery: Risks and Recommendations — Dr. Christine Ren-Fielding
UncategorizedMore Doctors are Recommending Bariatric (Weight Loss) Surgery as a Safe and Effective Treatment for Obesity
In considering weight-related treatments for patients, one metric that doctors such as Dr. Christine Ren-Fielding use is body mass index (BMI). This computation is a ratio of a person’s weight to height used to estimate a person’s body mass. In cases of obesity or morbid obesity, one treatment that is growing in popularity is bariatric (weight loss) surgery. Although surgical intervention may seem a radical suggestion for weight loss, bariatric surgery risks are quite low. They’re also significantly less compared to the long term risks of remaining obese and developing additional related health complications.
Body Mass Index (BMI)
Body mass index (BMI) is calculated by dividing a person’s weight in kilograms by their height squared. Although this number alone isn’t an indicator of overall health, doctors like Dr. Christine Ren-Fielding find it to be a good metric for tracking progress during and after weight loss strategies. (You can calculate your body mass index here.)
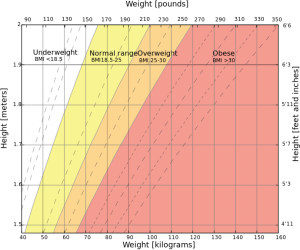
Bariatric (weight loss) surgery may be recommended for patients categorized as obese or morbidly obese. Bariatric surgery risks are less than the life-threatening complications likely to arise if obesity is never treated.
The above categorization is helpful in determining a course of treatment and is part of the guideline for recommending bariatric surgery. It’s recommended for obese or morbidly obese patients who have had difficulty losing weight by diet and exercise alone, especially if there is at least one comorbidity.
Bariatric (Weight Loss) Surgery is Less Risky than Complications Arising From Obesity
There are numerous life-threatening health conditions that can arise from untreated obesity. Heart disease, stroke, type 2 diabetes, sleep apnea, and certain types of cancers are more prevalent in conjunction with obesity. Chronic physical pain and discomfort are also common due to excess weight, as are psychological issues such as anxiety and depression.
Recent studies have shown bariatric surgery to be an excellent means of achieving and sustaining weight loss. Although surgery seems like a drastic option, experts now believe that the health complications from obesity are for more of a risk than undergoing bariatric surgery. Risks are associated with any surgical procedure, obviously, but current bariatric (weight loss) surgery procedures are now no riskier than gall bladder surgery and can also resolve existing comorbidities, such as type 2 diabetes.
For a Consultation with Dr. Christine Ren-Fielding
If you are struggling with obesity and related health complications, or would like more information about bariatric surgery, risks, and other recommendations, please contact Dr. Christine Ren-Fielding at the NYU Langone Weight Management Program.
No comments yet.